TEAM Project » Design Innovations » Lighting Strategy in Factory Designs
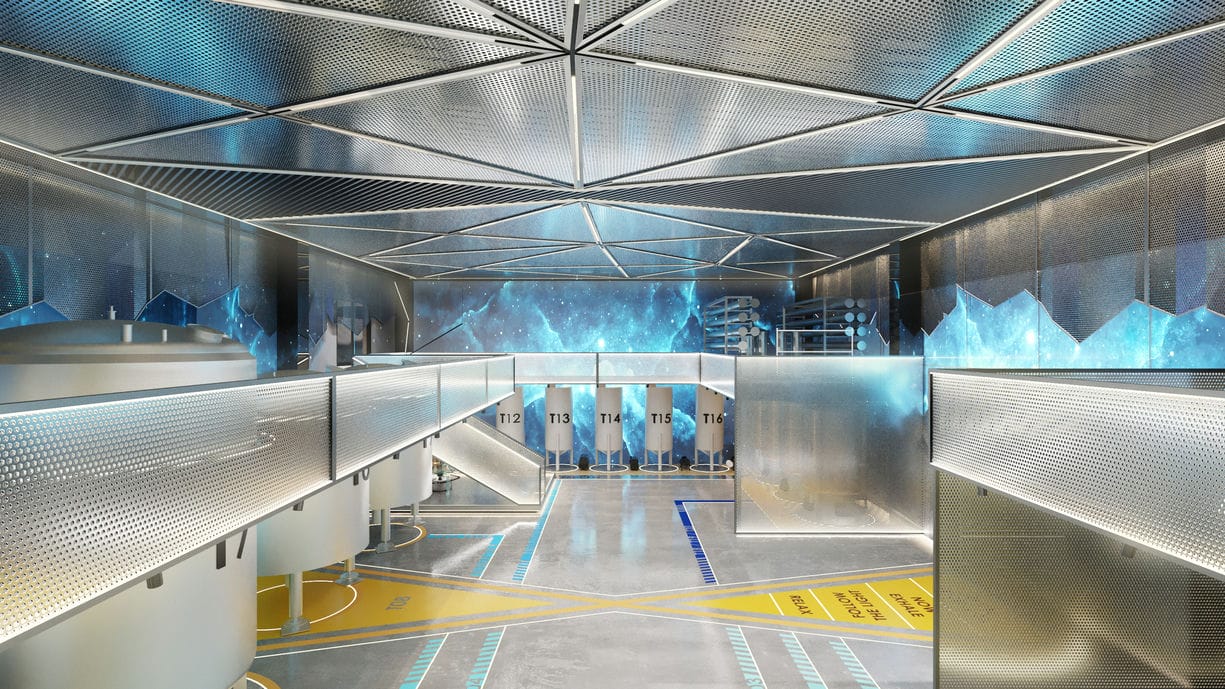

Lighting Strategy in Factory Designs
Lighting strategy in factory designs not only ensures visual comfort and workplace safety but also enhances production efficiency and the overall well-being of employees. A well-planned lighting system optimizes work processes while supporting energy efficiency. In this article, we will discuss the key elements to consider in lighting strategy for factory designs, including the integration of natural and artificial lighting, energy efficiency, and sustainability.